مجلات علمية
2021 ESC Guidelines for the determination and therapy of intense and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the conclusion and therapy of intense and ongoing cardiovascular breakdown of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the unique commitment of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC1.
Guidelines brief and examine to be had proof with the intention of helping fitness specialists in providing the exceptional control techniques for a man or woman affected person with a given condition. Guidelines and their guidelines ought to facilitate selection making of fitness specialists of their day-by-day practice. However, the very last selections regarding a man or woman affected person need to be made with the aid of using the accountable fitness professional(s) in session with the affected person and caregiver as appropriate.
The aim of this ESC Guideline is to help wellbeing experts oversee individuals with heart failure (HF) as per the best accessible proof. Luckily, we presently have an abundance of clinical preliminaries to assist us with choosing the best administration to work on the results for individuals with HF; for some, it is currently both preventable and treatable. This rule gives pragmatic, proof-based proposals. The configuration of the past 2016 ESC HF Guidelines was amended to make every aggregate of HF independent as far as its analysis and the executives. The treatment proposals notice the treatment impact upheld by the class and level of proof and are introduced in tables. In this rule, we have chosen to zero in on the determination and treatment of HF, not on its anticipation.
Definition of coronary heart failure
Cardiovascular breakdown is certifiably not a solitary obsessive determination, yet a clinical disorder comprising of cardinal side effects (for example windedness, lower leg expanding, and weakness) that might be joined by signs (for example raised jugular venous tension, pneumonic pops, and fringe oedema). It is expected to an underlying as well as useful irregularity of the heart that outcome in raised intracardiac pressures or potentially lacking cardiovascular yield very still and additionally during exercise.
Right ventricular dysfunction
Heart failure also can be an end result of proper ventricular (RV) disorder. RV mechanics and feature are altered withinside the placing of both strain or quantity overload.sixteen Although the principle aetiology of continual RV failure is LV disorder-precipitated pulmonary hypertension, there are some of different reasons of RV disorder [e.g. MI, arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), or valve disease].17 The prognosis is decided through a quantitative evaluation of world RV feature, maximum typically through echocardiography, the use of as a minimum one of the following measurements: fractional region change (FAC); tricuspid annular aircraft systolic excursion (TAPSE); and Doppler tissue imaging-derived systolic S′ pace of the tricuspid annulus. The prognosis and control of RV disorder is included comprehensively in a latest Heart Failure Association (HFA) function paper.2
Other normal wording utilized in cardiovascular breakdown
Heart failure is normally separated into two presentations: chronic heart failure (CHF) and acute heart failure (AHF). CHF portrays the people who have had a set up analysis of HF or who have a more progressive beginning of indications. In the event that CHF falls apart, either unexpectedly or gradually, the scene might be depicted as 'decompensated' HF. This can bring about an emergency clinic affirmation or treatment with intravenous (i.v.) diuretic treatment in the outpatient setting. Moreover, HF can introduce all the more intensely. Both of these are considered in the part on AHF.
Phrasing identified with the indicative seriousness of heart failure
The least complex wording used to portray the seriousness of HF is the New York Heart Association (NYHA) practical order. Notwithstanding, this depends entirely on side effects and there are numerous other better prognostic markers in HF. Importantly, patients with gentle indications might in any case have a high danger of hospitalization and death. Predicting result is especially significant in cutting edge HF to direct determination of cardiovascular transplantation and gadget treatments. This will be canvassed exhaustively in the part on cutting edge HF3.
Key steps in the determination of chronic heart failure
The conclusion of CHF requires the presence of indications as well as indications of HF and target proof of heart brokenness. Common manifestations incorporate shortness of breath, exhaustion, and lower leg expanding. Indications and signs need adequate exactness to be utilized alone to make the analysis of HF.4
The finding of CHF is made almost certain in patients with a background marked by MI, blood vessel hypertension, CAD, diabetes mellitus, liquor abuse, constant kidney infection (CKD), cardiotoxic chemotherapy, and in those with a family background of CMP or unexpected demise.
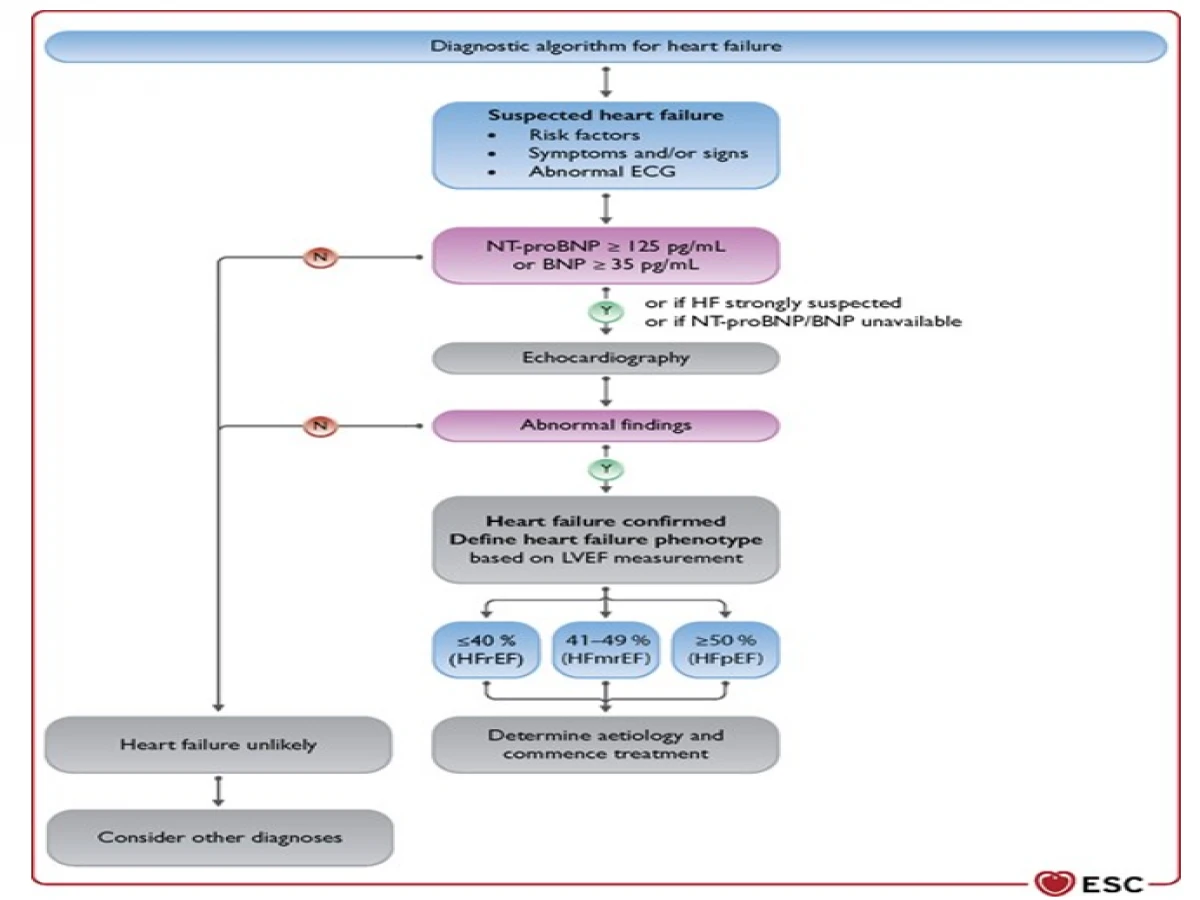
The diagnostic algorithm for heart failure1.
The determination of heart failure with decreased discharge portion
The finding of HFrEF requires the presence of manifestations or potentially indications of HF and a decreased discharge portion (LVEF ≤40%). This is most as a rule acquired by echocardiography. Insights regarding the quality principles that ought to be clung to while deciding the presence of diminished LV systolic capacity by echocardiography can be found in the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) position paper.5 If evaluation of EF is preposterous by echocardiography, then, at that point, CMR or seldom, atomic procedures can be utilized.
Therapeutic algorithm of Class1
General standards of pharmacotherapy for heart failure with diminished discharge division
Modulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAAS) and thoughtful sensory systems with angiotensin-changing over compound inhibitors (ACE-I) or an angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), beta-blockers, and mineralocorticoid receptor adversaries (MRA) has been displayed to further develop endurance, lessen the danger of HF hospitalizations, and diminish side effects in patients with HFrEF. These medications fill in as the establishments of pharmacotherapy for patients with HFrEF. The group of three of an ACE-I/ARNI, a beta-blocker, and a MRA is suggested as foundation treatments for these patients, except if the medications are contraindicated or not tolerated.6 They ought to be uptitrated to the portions utilized in the clinical preliminaries (or to maximally endured dosages in case that is unimaginable). This rule actually suggests the utilization of ARNI as a trade for ACE-I in reasonable patients who stay indicative on ACE-I, beta-blocker, and MRA treatments; nonetheless, an ARNI might be considered as a first-line treatment rather than an ACE-I.6 The suggested dosages of these medications are given in Table 8. Angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) actually play a part in the individuals who are narrow minded to ACE-I or ARNI.
Medications suggested in all patients with heart failure with decreased launch part1
· Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
· Beta-blockers
· Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists
· Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor
· Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors
Other medications prescribed or to be considered in chose patients with cardiovascular breakdown with decreased launch part
· Diuretics
· Angiotensin II type I receptor blockers
· If-channel inhibitor
· Combination of hydralazine and isosorbide dinitrate
· Digoxin
· Recently reported advances from trials in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
Significant advances in the determination and treatment of patients with HF have happened over ongoing years. Solid proof for new treatment choices have been given by ongoing RCTs and HF the board might go through significant changes before very long. New revelations, nonetheless, present new difficulties and numerous regions with absence of proof actually remain. Coming up next is a short rundown of chose, normal issues that have the right to be tended to in future clinical examination1.
For patients with HF, QIs might help medical services suppliers to all the while operationalize discrete guideline recommendations and empower the separation between botched freedoms and proper consideration. Besides, QIs permit the catch of patients' experience. Accordingly, and in corresponding with the composition of these rules, a set-up of QIs for the assessment of care and results for patients with HF was created.
References
1. https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/42/36/3599/6358045
2. Gorter TM, van Veldhuisen DJ, Bauersachs J, Borlaug BA, Celutkiene J, Coats AJS, Crespo-Leiro MG, Guazzi M, Harjola VP, Heymans S, Hill L, Lainscak M, Lam CSP, Lund LH, Lyon AR, Mebazaa A, Mueller C, Paulus WJ, Pieske B, Piepoli MF, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, Seferovic PM, Solomon SD, Shah SJ, Triposkiadis F, Wachter R, Tschöpe C, de Boer RA. Right heart dysfunction and failure in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: mechanisms and management. Position statement on behalf of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018 Jan;20(1):16-37.
3. Caraballo C, Desai NR, Mulder H, Alhanti B, Wilson FP, Fiuzat M, Felker GM, Piña IL, O'Connor CM, Lindenfeld J, Januzzi JL, Cohen LS, Ahmad T. Clinical Implications of the New York Heart Association Classification. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Dec 3;8(23): e014240.
4. Kelder JC, Cramer MJ, van Wijngaarden J, van Tooren R, Mosterd A, Moons KG, Lammers JW, Cowie MR, Grobbee DE, Hoes AW. The diagnostic value of physical examination and additional testing in primary care patients with suspected heart failure. Circulation. 2011 Dec 20;124(25):2865-73.
5. Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA, Kuznetsova T, Lancellotti P, Muraru D, Picard MH, Rietzschel ER, Rudski L, Spencer KT, Tsang W, Voigt JU. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015 Mar;16(3):233-70.
6. Gayat E, Arrigo M, Littnerova S, Sato N, Parenica J, Ishihara S, Spinar J, Müller C, Harjola VP, Lassus J, Miró Ò, Maggioni AP, AlHabib KF, Choi DJ, Park JJ, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Januzzi JL Jr, Kajimoto K, Cohen-Solal A, Mebazaa A; GREAT Network. Heart failure oral therapies at discharge are associated with better outcome in acute heart failure: a propensity-score matched study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018 Feb;20(2):345-354.