مجلات علمية
Cellulitis definition
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the skin and underlying tissues such as muscles and fascia, and appears as expanding redness, swelling, and warmth in the affected area, in which the bacteria enter and cause infection [1], It mostly affects the skin of the lower legs [2], Cellulitis affects about 14 and a half million in the United States alone every year, which costs it very much. [3]
Causes of cellulitis
Deep wounds or infections resulting from operations wounds or accidents resulting from traffic accidents, as well as severe bone injuries, all of these reasons may lead to bacteria reaching the tissues of the skin and epidermis.[1]
causative organisms:
group A streptococci (Streptococcus pyogenes) It is the first cause of cellulitis, and infection may occur in more than one type, such as Staphylococcus aureus, but less commonly. [3]
Risk factors for cellulitis:
uncontrolled diabetes
Injuries and skin diseases such as eczema and any disease that causes skin ulcers
Liver diseases such as cirrhosis or viral hepatitis
Problems with the circulatory system or lymphatic system [1]
Symptoms
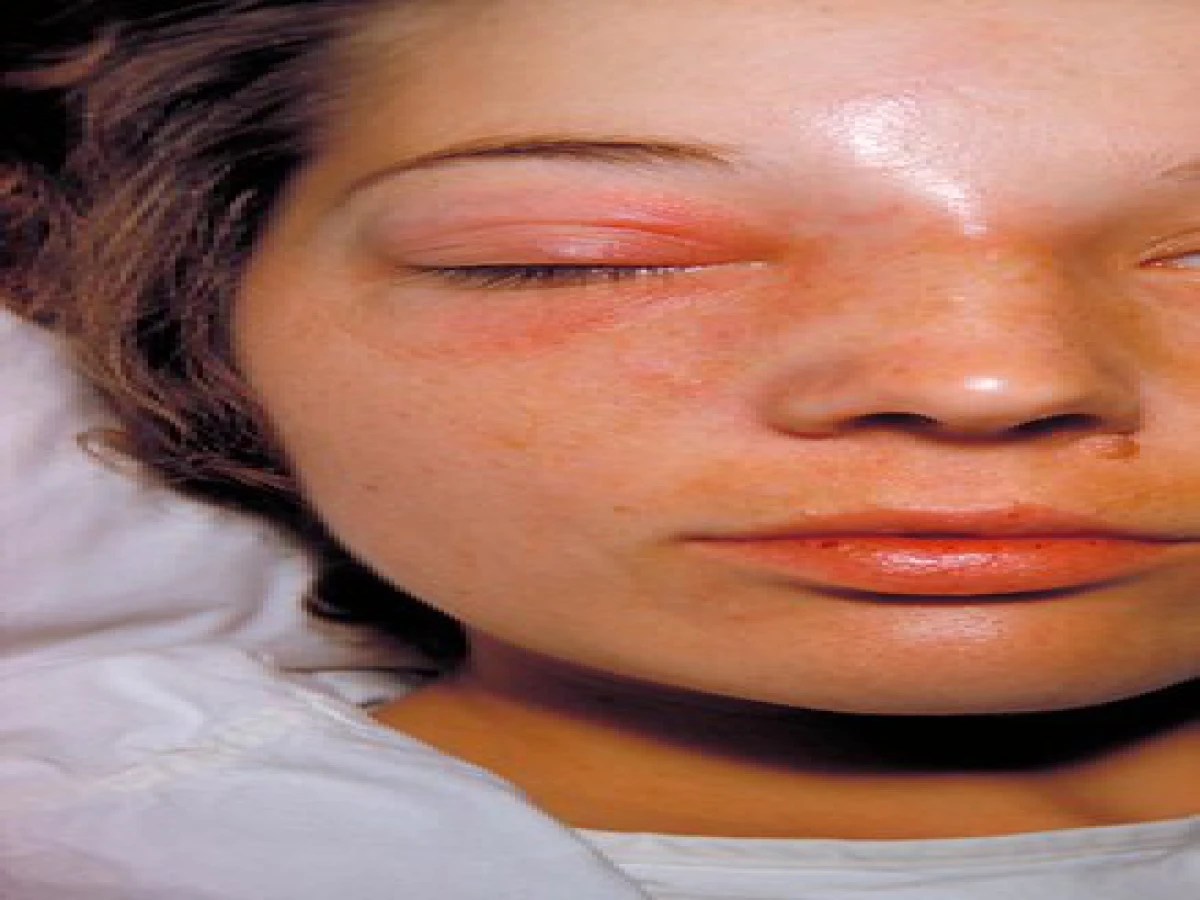
Cellulitis appears in the form of non-specific and painful redness, swelling appears on the affected area in which bacteria have penetrated the skin barrier (fig 1) [4], blisters may appear on the affected area with skin numbness in it, high temperature may coincide with cellulitis, as well as in some cases it may appear feeling sick. [1]
Diagnosis and investigations
When symptoms of cellulitis appear, laboratory tests and x-rays are performed to confirm the correct diagnosis and start treatment quickly:
A bacteria culture is performed to ascertain the type of bacteria that caused the infection, and then an antibiotic sensitivity test is conducted to select the appropriate antibiotic.
An x-ray is done to make sure that there are no complications in the bones
A complete blood count is performed to check whether the bacteria have reached the blood or not and to follow up on complications.[1]
Treatment
The drug is selected according to the stage, the progress of the disease and it’s spread to other organs:
In the case of simple cellulitis or that has not spread to the surrounding tissues and there is no fever, we can use oral antibiotics for a period of up to two weeks, often and improvement begins to appear and may be cured within 7 to 10 days from the beginning of treatment [5]
If the patient does not improve after 3 days of starting oral antibiotics, or if the infection is accompanied by a high temperature than normal, or the infection has spread to the deep tissues, sepsis, or a severe drop in blood pressure, then he is booked in the hospital and given medications by intravenous injection, which speeds up recovery and improve the condition before it reaches a serious condition. [5]
Sometimes surgery may be needed to remove pus and dead tissue from the infection. [2]
Finally, we can prevent the occurrence of cellulitis from the beginning by cleaning and disinfecting wounds, using topical antibiotics such as ointments, and changing dressings frequently to ensure they are clean. [2]
Complication
Many complications may occur due to leaving cellulitis untreated, including the arrival of bacteria to vital living tissues such as blood, bones, joints and veins, causing:
Sepsis and bacteremia
joint inflammation
Clots within veins caused by a blood clot
Endocarditis [4]
References
https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/guide/cellulitis
https://www.healthline.com/health/cellulitis
A. B. Raff, & D. Kroshinsky, Cellulitis. JAMA, 316(3), 325. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.8825 (2016).
https://www.cdc.gov/groupastrep/diseases-public/Cellulitis.html
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cellulitis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20370766