مجلات علمية
.webp)
Lymphoma overview
It is a tumor that appears in the infection-fighting cells of the immune system that causes cells to grow outside their range in the body and they are called lymphocytes. They are found in the lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen, and thymus gland.[1]
Predisposing factors
Scientists have not been able to identify most of the leading causes of the disease, but they have identified some of the leading causes of the disease [2]
Old age, people over the age of sixty are more susceptible to disease than others [1]
people who suffer from an immune disease such as AIDS, rheumatoid arthritis, and digestive infections are more susceptible than others.[1]
The tumor develops when the white blood cells undergo a genetic change, and this change leads to rapid cell growth and the accumulation of diseased cells in the body
Genetic change that appears on cells with age, weakening of the immune system, infection and viruses, and men are more susceptible to tumors in the lymph nodes than women. [1]
Prevalence of lymphoma
In a study conducted in 2012, the number of people infected with this type of cancer reached 5,700 patients within 8 years in the United Kingdom.[3]
Symptoms
Many people with tumor do not initially have symptoms, but as the tumor progresses and spreads, some symptoms appear, such as fever, fatigue, tiredness, night sweats, enlarged lymph nodes and an enlarged spleen, which causes pain in the upper left part of the abdomen and weight loss, the most important 2 signs is enlarged lymph nodes and enlarged spleen.[1][2]
Gross picture
Lymphoma presents as swollen lymph nodes) fig 1) and when clipped and examined it appears as a fish-flesh-like cut surface with a light pinkish tan [4]
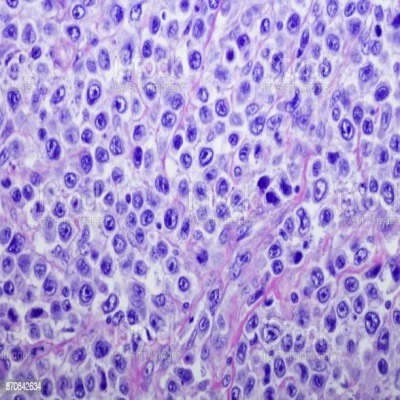
Microscopic picture
In the microscopic section of 's lymphoma, polymorphous cancer cells appear. Cancer cells in the case of lymphoma are called Reed-Sternberg cells, and they are characterized by a large nucleus and they are rich in cytoplasm (fig 2) and surrounded by lymphocytes and macrophages.[5]
Diagnosis
The doctor performs a physical examination of the lymph nodes in the groin, axilla and neck, in addition to enlargement of the spleen and liver
Your doctor recommends taking a sample for laboratory testing, taking a sample of bone marrow, and analyzing the sample to look for lymphocytes, The number of swollen cells in the blood sample may indicate your diagnosis
Your doctor may recommend an imaging test to check that there is no tumor in other areas of the body, including an MRI and CT scan. [2]
Treatment
The method of treatment varies from one patient to another, due to the different stage of the disease and general health, and the goal of treatment is to destroy cancer cells
Stages of treatment for swollen lymph nodes
active monitoring
There are some forms of swelling of the slow-growing lymph nodes. The doctor may decide to wait until the lymphoma is treated when signs appear that affect the patient's daily activity
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses medicines to kill fast-growing cells. The patient takes medicines intravenously. There are also tablets
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high energy, such as X-rays, to kill cancer cells[2]
prognosis
According to studies conducted, the 5-year relative survival rate was calculated as 91% in the localized type and about 81% in the distant species, which are high survival rates.[7]
References
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/lymphoma/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352642
A. Smith, S. Crouch, S. Lax, et all Lymphoma incidence, survival and prevalence 2004–2014: sub-type analyses from the UK’s Haematological Malignancy Research Network. British journal of cancer, 112(9), 1575-1584. (2015)
https://medpics.ucsd.edu/index.cfm?curpage=image&course=path&mode=browse&lesson=6&img=50
https://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=4&Case=379
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/hodgkin-lymphoma/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-rates.html